Phytochemicals in Apples
Phytochemicals are organic compounds found in fruits, vegetables and other plants that have biological activity in the body.
The average phenolic content of a 100 gram apple varies from 110 to 347 milligrams and it is estimated that about 20% of all healthy fruit phenolics consumed in the United States comes from apples.
It is expected that apple cider vinegar, made from whole fresh apples, will also contain a good portion of these beneficial compounds.

Researchers are just starting to understand which phytochemicals found in apples and other fruits and vegetables are responsible for their various health benefits.
This is no small task since it is estimated that there are thousands of different phytochemicals in a typical fruit or vegetable.
Chemically, most phytochemicals include many regularly alternating single-bonbed and double-bonded carbon atoms.
This structure allows these organic molecules to absorb light in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum causing them to be highly colored and at the same time giving them antioxidant properties.
 The more intense the color of a fruit or vegetable the greater the concentration of these health promoting compounds.
Use this fact the next time you are picking-up fruits and vegetables, and chose the more highly colored ones (usually organic or home grown) to get the highest level of phytochemicals.
The more intense the color of a fruit or vegetable the greater the concentration of these health promoting compounds.
Use this fact the next time you are picking-up fruits and vegetables, and chose the more highly colored ones (usually organic or home grown) to get the highest level of phytochemicals.
For the apple, most of these colorful compounds are concentrated in the skin.
Recently, thirteen triterpenoid type compounds were extracted from Red Delicious apple peels and evaluated in a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
These triterpenoids were found to be potent against the following three types of human cancer cells: breast, colon, and liver.
This research shows that the apple peel contains most of the apple's phytochemical compounds which may account for most of its anticancer properties.
Reference: Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, Vol. 55, No. 11, May 30, 2007: 4366-4370. (
Web Link
)
Examples of
Apple Phytochemicals
So what is the difference between a flavonoid or a polyphenyl and a triterpenoid?
Specific examples of organic compounds from these three classes of phytochemicals found in apples are shown below along with some of their health benefits:
1) Flavonoids
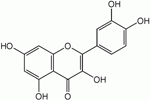
Apples are rich in Quercetin which is a type of phytochemical called a flavonoid.
Quercetin has shown strong anti-inflammatory activity, it inhibits both the manufacture and release of histamine and other allergic / inflammatory compounds.
Quercetin also shows significant anti-tumour properties with respect to skin and prostate cancers.
Another flavonoid found in apples is Catechin, although the largest source in the human diet is from various teas.
Catachins, specifically epicatachin, has been found to reduce the risk of stroke, heart failure, cancer and diabetes.
Cyanidin, another flavonoid or anthocyanin type phytochemical, is found in apples as well as in many types of redberries and in red cabbage.
It also is an antioxidant which protects cells from oxidative damage thereby reducing the risk of heart disease and cancer.
2) Polyphenols
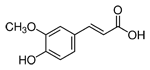
Ferulic acid is a phenolic phytochemical which is present in apples and many plant cell walls and seeds.
This compound has significant antioxidant and anti-cancer activity and may neutralize free radicals which can be involved in DNA damage and accelerated cell aging.
3) Triterpenoids
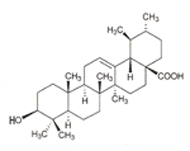
Ursolic acid, a pentacyclic triterpenoid, is also found in many other plants and fruits besides apples, including cranberries, prunes, peppermint, lavender, oregano and thyme.
This phytochemical inhibits tumor growth, and also has anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial properties.
As a result, ursolic acid has demonstrated medicinal action both internally and topically
and is used in ointments to treat burns.